Chapter 5: Bloodborne – Protection from Pathogens

Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are microorganisms found in blood or other bodily fluids that can cause diseases if they enter the body. Protecting oneself from exposure to these pathogens is vital.
Here are essential steps to safeguard against bloodborne pathogens:
Ensuring Safety:
Always prioritize safety by assessing the scene before any action. Identify visible blood contamination and take precautions accordingly to avoid exposure to Bloodborne Pathogens (BBPs).
Universal Precautions:
OSHA mandates Universal Precautions, a strategy to safeguard employees from potential exposure to all human blood and Other Potentially Infectious Materials (OPIM). Treat all blood and OPIM as though they contain BBPs, including HIV, to minimize risks of infection.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Utilize Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) when handling blood or OPIM:
– Gloves
– Goggles (eye protection)
– Gowns, lab coats, or aprons
– Caps
– Shoe covers
– Face shields/masks
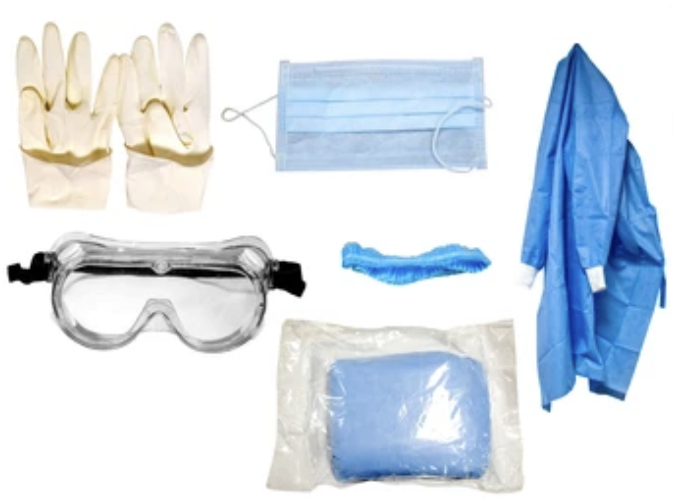
Select PPE based on exposure type and anticipated quantity of blood or OPIM as per your company’s exposure control plan.
Safe Handling and Disposal:
– Dispose of contaminated materials properly in labeled, leak-proof, and puncture-resistant containers.
– Never recap, bend, or break needles after use; dispose of them in appropriate sharps containers.
– Use caution when handling or transporting sharps to prevent accidental injury.
Hand Hygiene:
– Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after removing gloves or other PPE.
– Use alcohol-based hand sanitizers if soap and water are unavailable.
Safe Practices:
– Avoid eating, drinking, applying cosmetics, or handling contact lenses in areas where exposure to blood or OPIM is possible.
– Never store food or drink in refrigerators, freezers, shelves, cabinets, or on countertops or benchtops where blood or OPIM are present.
– Understand the risks associated with occupational exposure and know the proper steps to protect oneself and others.
Emergency Procedures:
– Have access to first aid supplies and know the appropriate actions to take in case of an exposure incident.
– Follow company procedures or protocols in the event of accidental exposure.
Remember, always adhere to workplace guidelines and safety protocols regarding bloodborne pathogens. If you experience a potential exposure incident, seek immediate medical attention and report it according to your organization’s policies.
Please note that this information is for educational purposes only and should not substitute professional medical advice or guidance.
Protecting yourself from bloodborne pathogens is crucial to prevent potential exposure and subsequent health risks.
Other Standard Precautions:
Maintain specific hygiene protocols to minimize risks:
– Avoid eating, drinking, or smoking in potentially contaminated areas.
– Thoroughly cleanse hands with soap and water after contact with body fluids or use antiseptic hand sanitizers/cleansers.
– Handle biohazard waste containers cautiously to avert exposure.
Handling Biohazard Waste:
Dispose of needles, sharps, and potentially infectious materials in designated containers with proper labels. Follow workplace guidelines for proper disposal, ensuring compliance with regulations.
Biohazard waste containers should be labeled with a fluorescent orange or orange-red background and the international biohazard symbol.
Employ engineering and work practice controls, such as sharps disposal containers and safer medical devices, as recommended by OSHA to reduce or eliminate employee exposure.
Adhering to these measures is essential for safeguarding against bloodborne pathogens and minimizing the risks associated with potential exposure in the workplace.