Chapter 3: Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart in PALS

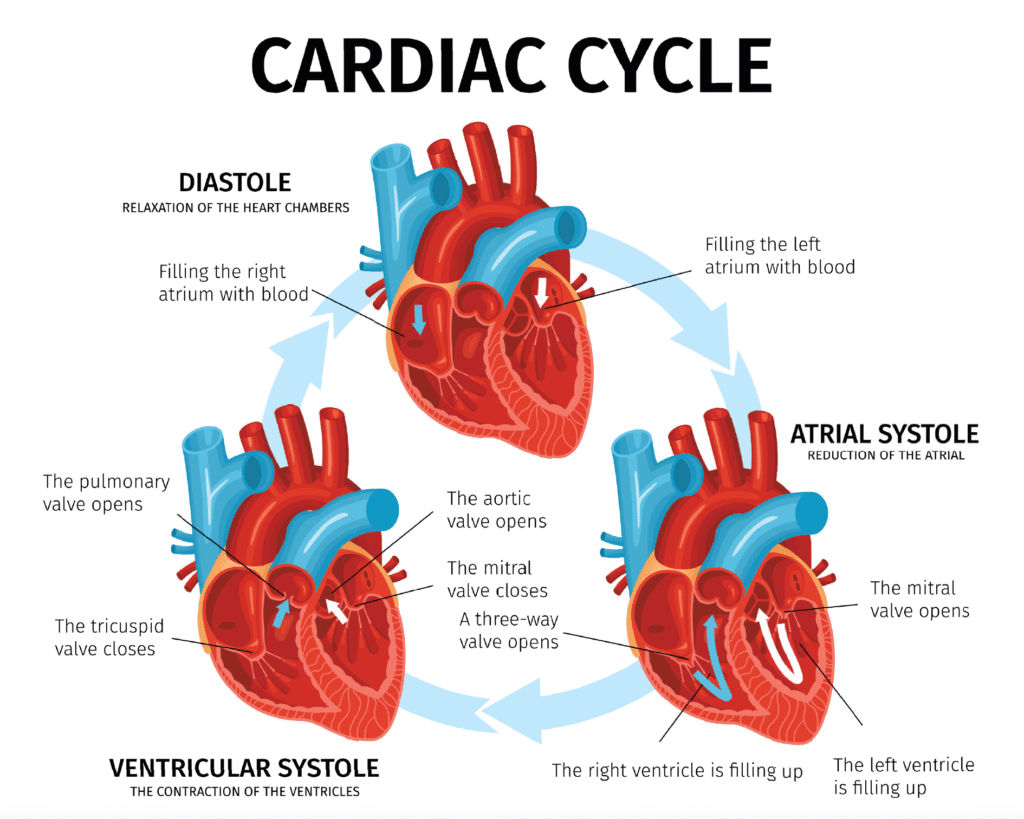
Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the heart is essential in Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) as it provides the foundation for assessing and managing cardiac emergencies in pediatric patients. The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest cavity and is divided into four chambers: two atria and two ventricles.
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cavae. It then contracts, pumping blood through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. From there, the right ventricle pumps blood through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery, which carries it to the lungs for oxygenation.
Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium via the pulmonary veins. The left atrium contracts, forcing blood through the mitral valve into the left ventricle. The left ventricle is the heart’s main pumping chamber, responsible for ejecting oxygen-rich blood into the aorta through the aortic valve. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
The heart’s electrical system, which controls its rhythm and contraction, is coordinated by specialized cells. The sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the right atrium, serves as the heart’s natural pacemaker, initiating electrical impulses that stimulate atrial contraction. The impulses then travel through the atrioventricular (AV) node and specialized conduction pathways (the bundle of His and Purkinje fibers) to the ventricles, triggering ventricular contraction.
In PALS, understanding normal cardiac anatomy and physiology helps healthcare providers recognize abnormal rhythms and disturbances in pediatric patients. For example, knowledge of the normal electrical conduction pathway aids in identifying arrhythmias such as supraventricular tachycardia or heart blocks. Additionally, understanding the heart’s function helps guide interventions such as defibrillation, medication administration, and advanced airway management during resuscitation efforts.
Overall, a thorough understanding of the anatomy and physiology of the heart is fundamental in PALS, enabling healthcare providers to effectively assess, manage, and treat pediatric cardiac emergencies and improve outcomes for critically ill or injured children.